Walk-Behind Power Trowel vs. Ride-On Power Trowel: Which One Is Right for Your Job?
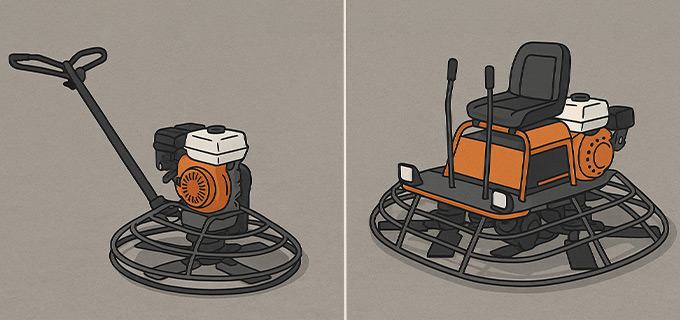
Concrete finishing plays a vital role in construction, impacting the slab’s strength, longevity, and overall appearance. To achieve a smooth, level, and polished concrete surface, contractors often rely on power trowels, also known as power floats. These machines automate the backbreaking labor of hand troweling, allowing for faster and more consistent results. But when it comes to choosing the right equipment, contractors face a common dilemma: walk-behind vs. ride-on power trowels. As a manufacturer of power trowels, one common question we hear is: Which type is better? The answer depends on various factors such as project size, labor availability, budget, finish requirements, and maneuverability. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through the key differences, benefits, limitations, and ideal use cases of both types of trowels to help you make an informed decision. What Is a Walk-Behind Power Trowel? With a walk-behind power trowel, a person walks behind the machine to guide it across the concrete surface. It typically features one or two rotors with troweling blades that rotate at high speed to finish the surface. Walk-behind trowels are available in a range of sizes, usually between 24 to 48 inches, and are popular for small to medium-scale projects. Key Features: Single or twin-blade rotor Manual throttle control or dead-man switch Gasoline, diesel, or electric engines Lighter weight and easier to transport Suitable for confined areas and edges Pros and Cons ✅ Lower initial cost ❌ Lower productivity ✅ Easier to maneuver ❌ Labor-intensive ✅ Simple operation ❌ Operator fatigue ✅ Lightweight design ❌ Not suitable for large slabs ✅ Low maintenance ✅ Portable What Is a Ride-On Power Trowel? A ride-on power trowel, on the other hand, allows the operator to sit and steer the machine using levers or joystick controls. These machines are equipped with dual rotors and are significantly larger, making them ideal for large-scale commercial or industrial floors. Key Features: Operator-controlled steering from a seated position Twin rotors for wider coverage (typically 36 to 60 inches each) Hydraulic or mechanical steering More powerful engines (up to 35 HP or more) Ideal for covering large areas quickly Pros and Cons ✅ High Productivity ❌ High Cost ✅ Superior Finish Quality ❌ Large Size ✅ Reduces Operator Fatigue ❌ Requires Training ✅ Dual-Rotor Options ❌Higher Maintenance ✅ Improved Efficiency Performance Comparison Let’s examine how walk-behind and ride-on power trowels differ across several important criteria. Surface Area Coverage Walk-Behind: Best suited for smaller pours under 3,000 square feet. With narrower blades, it requires more time and passes to complete the surface. Ride-On: Intended for huge spaces over 3,000 square feet. A dual-rotor ride-on machine can cover up to 10,000 sq. ft. per day. ✅ Winner: Ride-on (in terms of productivity) Maneuverability Walk-Behind: Offers excellent control in tight spaces, corners, and around columns or forms. Ideal for intricate jobs. Ride-On: Struggles in confined areas and cannot reach edges. Requires follow-up hand troweling or a walk-behind for perimeter work. ✅ Winner: Walk-behind (for precision and tight access) Speed and Efficiency Walk-Behind: Slower operation speed due to smaller size and manual control. Suitable for low-volume finishing. Ride-On: Significantly faster with broader coverage and higher blade speeds. Some models feature overlapping rotors for smoother transitions. ✅ Winner: Ride-on (faster completion on big jobs) Finish Quality Walk-Behind: Provides consistent finishes when used by skilled operators but may be less uniform over large areas. Ride-On: Delivers a high-gloss, professional finish with overlapping rotor models, especially with float pans attached. ✅ Winner: Ride-on (for uniform, mirror-like finish) Labor and Operator Fatigue Walk-Behind: Requires physical effort, especially over extended periods. Operator fatigue can affect finish quality. Ride-On: Reduces labor fatigue significantly, allowing operators to work longer shifts and focus on precision. ✅ Winner: Ride-on (for ergonomics and comfort) Transport and Storage Walk-Behind: Lightweight, compact, and easily transported in smaller trucks or trailers. Ride-On: Larger and heavier, requiring forklifts or ramps for transport. ✅ Winner: Walk-behind (for portability) Cost Comparison Initial Purchase Cost Walk-Behind: Ranges from $1,500 to $4,500 depending on size, engine type, and brand. Ride-On: Typically priced between $10,000 to $25,000, with some advanced hydraulic models costing more. Operating Costs Walk-Behind: Lower fuel consumption, simpler maintenance. Ride-On: Higher fuel usage and more complex components (hydraulics, dual engines) increase long-term maintenance needs. Labor Costs Walk-Behind: May require multiple operators for large pours. Ride-On: One operator can efficiently cover large areas, minimizing the need for additional labor. ✅ Winner: Walk-behind (for lower upfront cost), Ride-on (for long-term labor savings) Walk-Behind vs. Ride-On Power Trowel Comparison Feature Walk-Behind Power Trowel Ride-On Power Trowel Operation Style Manual (Walk Behind) Seated (Ride-On) Suitable Area Size Small to Medium (<5,000 sq. ft.) Large (>5,000 sq. ft.) Coverage Rate ~1,000–3,000 sq. ft./hour ~5,000–10,000+ sq. ft./hour Maneuverability High in tight spaces Limited in small or obstructed areas Finish Quality Moderate Superior (due to weight and blade power) Training Requirement Low Medium to High Operator Fatigue High (physical effort required) Low (ride-on comfort) Purchase Cost Lower (typically $1,000–$5,000) Higher (ranges from $8,000–$30,000+) Maintenance Requirement Simple More complex Best Use Case Small slabs, residential work Warehouses, industrial, commercial slabs When to Use a Walk-Behind Power Trowel Optimal use cases for a walk-behind trowel include: Domestic or small business applications Slabs with complex edges or obstacles Small spaces such as sidewalks, patios, driveways Contractors with tight budgets Beginners or teams without specialized training For instance, if you’re finishing a 1,200 sq. ft. residential garage slab, a 36-inch walk-behind trowel can effectively complete the task in a few hours without unnecessary investment. Ideal Situations for Using a Ride-On Power Trowel A ride-on trowel excels in: Large commercial or industrial floors Big-box retail stores, warehouses, factories Time-sensitive projects Jobs where top-tier flatness or FF/FL ratings are required Contractors working on regular, high-volume concrete pours If you’re tackling a 20,000 sq. ft. warehouse floor with a tight deadline, a dual-rotor ride-on trowel can complete the job several times faster than walk-behind units—and with better results. Operator Training and Safety Walk-behind power trowels are relatively straightforward to operate, and most workers can get up to speed with minimal