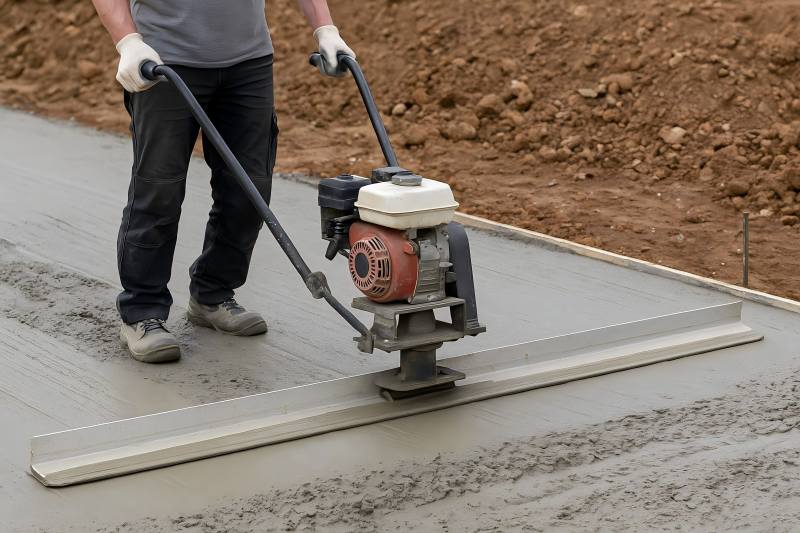
Troubleshooting Vibrating Screed Problems: Vibration, Blade Marks, Low Output
Vibrating screeds are essential tools for concrete contractors, offering faster leveling, reduced labor requirements, and smoother slab finishes compared to manual screeding. But like any construction equipment, vibrating screeds can experience problems that affect performance, surface quality, and productivity. When issues arise—such as excessive vibration, blade marks, and low output—contractors must understand the root causes and implement effective corrections to avoid rework, downtime, and uneven slabs. Understanding How Vibrating Screeds Work A vibrating screed uses a combination of blade length, weight, and vibration frequency to level and consolidate concrete. The motor (electric or gasoline) sends vibration through the blade, helping the concrete settle, expelling trapped air, and creating a relatively smooth surface. Key components include: Engine/motor (controls vibration frequency) Excentric weight or vibration module Screed blade (various lengths and thicknesses) Handle controls and throttle Mounting brackets and fasteners Any issue with these components can affect slab flatness, finishing time, and overall productivity. Most Common Vibrating Screed Problems Although vibrating screeds are simple machines, several issues can appear during operation: Excessive or Unstable Vibration The screed vibrates more aggressively than expected, becomes unstable, chatters across the surface, or becomes difficult to control. Blade Marks and Surface Imperfections Visible lines, dips, ripples, or chatter marks appear behind the screed blade. Low Output or Slow Productivity The screed completes fewer square meters per hour or struggles to move across the concrete. Uneven Concrete Density Some sections appear over-vibrated while others remain rough or loosely consolidated. Motor or Engine Issues Insufficient vibration, overheating, unstable RPM, or frequent stalling. Causes and Solutions for Excessive Vibration Excessive vibration often occurs when operators use overly long blades or poor-quality components. Uncontrolled vibration affects slab quality and operator fatigue. Common Reasons for Excessive Vibration Loose screws or fasteners in the mounting bracket or blade Worn or unbalanced vibration module Engine throttle too high Blade length too long for motor power Improper blade thickness Operator pushing the screed instead of letting it glide Incorrect vibration frequency for the concrete slump Solutions Tighten all screws, bolts, and connections before every use Inspect and replace vibration modules that show signs of wear Adjust throttle to recommended operating speed Use appropriate blade length (usually 2–4 m for handheld screeds) Choose a thicker blade (≥ 3 mm) to reduce chatter on stiff mixes Allow the screed to advance naturally—do not force it Reduce vibration frequency for dryer concrete mixes Causes and Solutions for Blade Marks and Surface Lines Blade marks—such as ripples, ridges, or chatter lines—are often the result of improper vibration frequency, incorrect blade selection, or poor operator technique. Common Reasons for Blade Marks Blade not level (front edge digging into concrete) Uneven concrete slump along the pour Blade too thin, causing deflection Vibration too low—not consolidating the surface Walking too fast and leaving behind ridges Blade worn or bent Concrete setting too fast in hot weather Operator lifting or tilting the blade unintentionally Solutions Check level and adjust handles to maintain consistent blade angle Use screening pipes or guides to maintain consistent pour depth Switch to a thicker blade for stiffer mixes or wide pours Increase vibration power to eliminate surface waves Slow down movement to allow proper settling Replace blades that are worn or bent Work with proper timing—avoid delays between concrete placement and screeding Maintain a stable grip and avoid tilting the blade during operation Causes and Solutions for Low Output Low output happens when the screed struggles to move forward or requires frequent rework. This reduces job efficiency and increases labor costs. Common Reasons for Low Output Insufficient motor power Worn vibration module producing weak vibration Blade width unsuitable for concrete slump Overly dry concrete mix causing drag Concrete placed unevenly ahead of the screed Operator not maintaining consistent pace Engine RPM too low Poor blade lubrication (dry blade dragging over concrete) Solutions Ensure the motor operates at recommended RPM Replace worn vibration modules Reduce blade length for low-slump concrete Adjust concrete mix moisture content Use proper raking and placement before screeding Maintain consistent forward motion Apply a light oil mist on the blade to reduce surface drag Troubleshooting Table: Vibrating Screed Problems and Solutions Below is a full troubleshooting table to help quickly identify issues on-site: Problem Likely Cause Solution Excessive vibration Loose fasteners Tighten all screws and bolts Unstable screed movement Overpowered throttle Reduce engine RPM Blade chatter marks Blade too thin Use thicker blade (≥ 3 mm) Ripples on surface Walking too fast Reduce pace Screed dragging Concrete too dry Add moisture or vibrate slower Uneven finish Blade angle incorrect Level the handle and readjust Low vibration Worn vibration module Replace module Slow productivity Blade length too long Switch to shorter blade Engine overheating Blocked airflow Clean engine and filters Stalling motor Low fuel or carburetor issue Refill and clean carburetor Selecting the Right Blade to Avoid Problems Blade selection is one of the most important aspects of preventing vibration issues, marks, and low efficiency. Blade Length Short blades (1–2 m): High precision, ideal for small areas Medium blades (2–3 m): Balanced performance for general slabs Long blades (3–4 m): High output but requires powerful engines and consistent slump Blade Thickness Thicker blades produce fewer chatter marks and remain more stable. Blade Thickness Best Use Characteristics 2–2.5 mm Thin concrete layers, small slabs Lightweight but prone to chatter 3 mm General construction Balanced performance 4–5 mm Low-slump or stiff mixes High stability and reduced blade marks Engine and Vibration Module Maintenance Tips Poor maintenance is a major contributor to vibrating screed performance problems. Follow these routine checks: Daily Maintenance Tighten all screws and bolts Clean concrete splatter off the engine and blade Check oil level (gasoline engines) Inspect the pull starter and throttle cable Test vibration frequency before starting work Weekly Maintenance Clean air filter Inspect the vibration module for wear Check blade straightness Inspect mounting brackets Monthly Maintenance Change engine oil Replace or clean the spark plug Inspect drive shaft or eccentric weights Operator Techniques That Prevent Problems Even a perfectly working screed will fail to deliver good results if operation is poor. Proper operator